TradFi, CeFi, and DeFi: Bridging the new frontier of the FinTech revolution on towards the stars

In this era of fast-paced advancements, change is the only constant. Nowhere is this change more apparent than in the sphere of finance. We see indelible shifts in structures and practices of financial transactions, as we move from traditional financing to embracing decentralized systems, marking a new epoch of finance.
Decentralized Finance, commonly known as DeFi, is pegged to be a revolutionary concept, charting an innovative course in the financial world. Whereas its counter-concept, Centralized Finance, or CeFi, provides a reminiscence of our traditional financial systems, acting as a necessary bridge. This blog post will delve deep into understanding these systems, comparing them, addressing the challenges they currently face, and exploring their future potential.
What is Traditional Finance (TradFi)
Traditional finance, also known as TradFi, serves as the backbone of our global financial ecosystem. It is the conventional financial system that has stood the test of time, since the dawn of civilization.
Originating centuries ago and evolving continually to meet the shifting needs of society, TradFi sets the groundwork for our understanding of finance. And being the original configurations of banking, lending, investment, and more, TradFi has shaped the economy as we know it. As the oldest form of the financial system, its systems are centralized, with primary control in the hands of various institutions that follow the regulatory frameworks per their jurisdiction.
Dominated by intermediaries like banks, stock exchanges, payment operators, and insurance companies, TradFi is heavily regulated by government bodies and institutions, leading to different regulatory frameworks across jurisdictions. The traditional sector encompasses some of the world’s largest markets, including foreign exchange, real estate, equities, derivatives, and commodities.
How TradFi works
TradFi functions within a highly centralized framework. Despite the digital solutions in place, core financial assets like balance sheets, order books, and transactions, are all managed by centralized entities or intermediaries. Most transactions happen under the control of these intermediaries with users having little to no control over their funds and assets.
There are limited peer-to-peer interactions, with most transactions being managed by intermediaries. As a result, users are often in a predicament where they need to trust these intermediaries with their assets and funds. Additionally, the rules are set forth by regulations, with intermediaries facilitating compliance. The banking sector’s reliance on the fractional reserve system, allowing them to lend much more than their held deposits, exemplifies this rule-dictated operation.
Under the TradFi paradigm, financial intermediaries act as bridges between investors and borrowers. They channel funds from areas of surplus to areas of deficit and, in doing so, create a system that impacts the entire economy. These institutions—banks, insurance companies, funds, etc.—determine the flow of credit through interest rates, using centralized systems to offer traditional services like loans, mortgages, and investments.
Security within TradFi is upheld via regulatory bodies and governmental oversight, minimizing systemic risk while providing consumers with a sense of trust in the institution handling their financial transactions: this control also reinforces compliance with rules and standards, enhancing stability in the global economy.
What is Centralized Finance (CeFi)
Centralized Finance, or CeFi, emerged out of the need for interaction with cryptocurrencies. Satoshi Nakamoto’s introduction of Bitcoin in 2009 as a decentralized money system, the first of its kind, revolutionized the financial ecosystem. Gradually, as Bitcoin and other altcoins gained traction, the need for a platform to exchange these digital assets led to the appearance of centralized exchanges (CeFI).
CeFi leverages traditional finance theories while incorporating digital assets like cryptocurrencies. Such platforms operate similarly to banks, serving as intermediaries between investors and borrowers but allowing transactions using both fiat and digital currencies.
Through these platforms, users can access a myriad of services, such as interest accounts, loans, and exchange currencies. These platforms provide an entry into the innovative world of cryptocurrency while maintaining the familiar comforts of traditional, centralized financial services.
How CeFi works
CeFi services function similarly to how traditional finance does—they’re managed by centralized intermediaries like exchange platforms. CeFi essentially brings traditional finance’s features to digital assets. Users need to place trust in crypto service providers and often end up relinquishing ownership of their crypto by holding the funds in hot wallets hosted by exchanges.
CeFi acts as a bridge linking the older world of TradFi with the emerging crypto markets, under a regulated framework by incorporating digital assets into the customary financial structure. Institutions in CeFi issue loans, facilitate crypto trading and allow users to earn interest on their assets.
However, the control still remains central. This means that unlike DeFi, user assets are not in their control, but in the custody of centralized platforms. This allows operations including crypto-to-fiat and/or crypto-to-crypto transactions, loan services, interest accounts, and staking, making CeFi an integral part of modern financial systems. CeFi, while simplifying processes such as crypto wallet management and key protection, takes in the role of a custodian, furthering the narrative of centralized control.
What is Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Decentralized finance, known as DeFi, appeared with the promise of decentralization. While the first DeFi concepts were proposed around 2013, but it wasn’t until 2020 that DeFi witnessed explosive growth. Adhering to the true principles of decentralization, DeFi positions power back into the hands of the user, emphasizing peer-to-peer collaboration.
Booming in the year 2020, DeFi gained the attention of traditional finance entities, realizing the potential to eliminate intermediaries and transferring control from centralized entities to communities. Despite its infancy, DeFi holds significant promise as a major disruptive force in the financial world.
DeFi marks a radical departure from its predecessors. It leverages blockchain’s distributed ledger technology and cryptocurrencies like Ethereum, with smart contracts automating financial transactions without middlemen. Emerging as an alternative to CeFi, DeFi promotes a more open and non-custodial financial system.
It offers services similar to those in TradFi and CeFi, like loans, interest accounts, and insurance, but without the need for intermediaries. The key attraction of DeFi lies in its decentralization—control lies with the user, not an institution.
How DeFi works
DeFi differs drastically from traditional financial systems in the sense that it’s a system built entirely on blockchain, facilitating crypto-economic protocols. Devised for interoperability, DeFi is based on public blockchains, allowing global access.
At its core, DeFi leverages cryptography, blockchain technology, and tokenomics to create an open and transparent financial system that is accessible to anyone with a smartphone and an internet connection. As a network of decentralized applications (DApps), DeFi aims to re-create and improve existing financial systems’ functions, such as lending and borrowing, insurance, asset trading, and more.
The DeFi ecosystem employs mechanisms unique to the world of finance, such as yield farming, liquidity mining, staking, and flash loans. It functions over Automated Market Makers (AMMs), lending protocols, yield farming, and DEXs—creating a comprehensive financial ecosystem without the need for intermediaries.

From an operational perspective, DeFi platforms function with less friction compared to traditional and centralized finance. By disintermediating financial transactions, it creates a permissionless ecosystem where anyone, regardless of geographical location or economic status, can access and participate in global finance.
Algorithms govern DeFi ecosystems, and the smart contracts guaranteeing transactions’ integrity are open-source, leading to a community-driven decision-making process. Users retain full custody of their assets and interact directly with the protocols. DeFi services span decentralized exchanges (DEXs), lending and borrowing platforms, yield farming, and more—all while offering users remain in absolute control of their assets.
TradFi vs CeFi vs DeFi
TradFi, CeFi, and DeFi each possess unique characteristics that distinguish them in their operation, risk levels, and yields. From a broad perspective, the main distinguishing factor among TradFi, CeFi, and DeFi is centralization and control. Each has its benefits and limitations; thus, a balance between them seems viable for a sustainable future.
In TradFi and CeFi, transactions are controlled by intermediary entities, be it banks or private firms. CeFi acts as a bridge between traditional finance and decentralized finance, providing features to transact with digital assets while retaining the structure of TradFi. Conversely, DeFi eliminates the need for middlemen, relying on blockchain technology and smart contracts to facilitate transactions.
TradFi, dictated by established financial institutions, offers security and a sense of familiarity but falls short of inclusivity and adaptability. On the other hand, CeFi tries to merge the best of both worlds, providing an amicable solution for those cautious yet intrigued by the brave new world of crypto.
DeFi, while nascent, poses a radical shift by democratizing access to financial services and enabling self-custody of assets, forging a pathway for a truly decentralized economic system. It provides users with full control of their assets and transactions, catering to the ethos of blockchain and crypto about decentralization and user control.
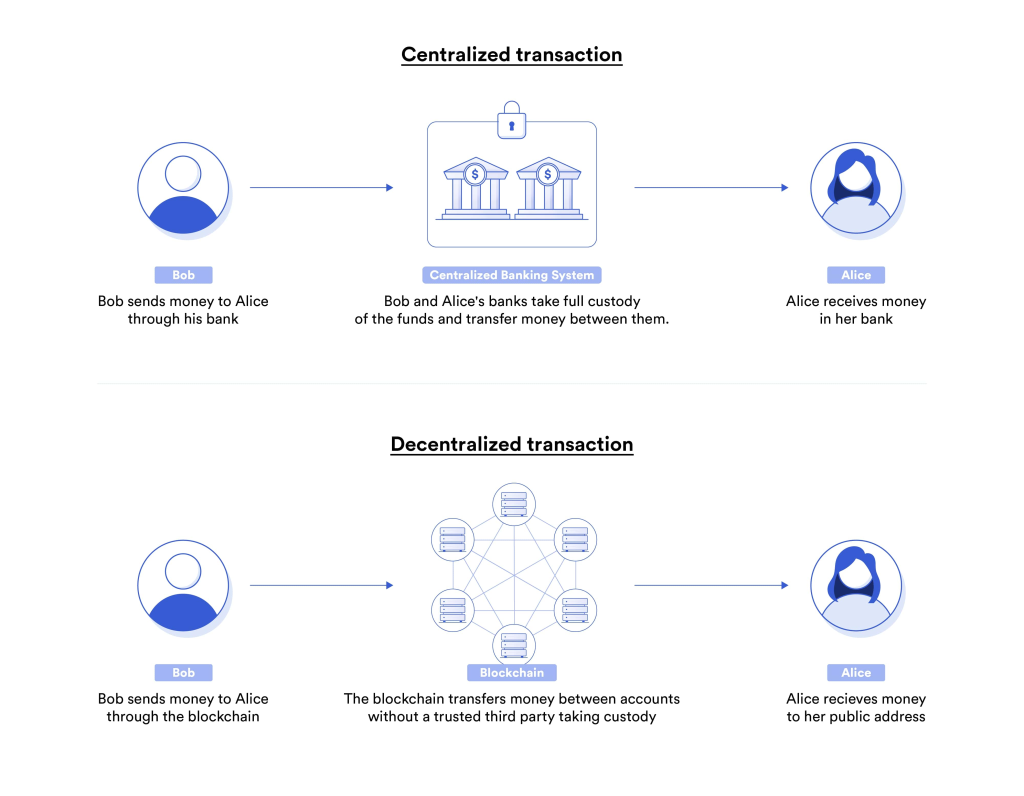
It leverages blockchain technology and smart contracts to ensure transparency and inclusivity. However, it also exposes users to risks synonymous with smart contracts and requires a certain level of technical knowledge to navigate. While TradFi and CeFi pose an issue with intermediary dependence, DeFi provides an advantage, allowing open and transparent transactions.
Comparatively, TradFi is highly regulated, ensuring consumer protection but potentially hindering innovation and accessibility. CeFi provides some regulatory safety but has been criticized for lack of transparency. On the other hand, DeFi is considered the Wild West of finance, given its minimal regulation, making it ripe for innovative solutions but also for potential scams and rogue players.

The Risks of DeFi and CeFi
To paint a clearer picture, let’s delve into some risks associated with DeFi and CeFi. Both DeFi and CeFi present unique risks alongside their benefits.
For DeFi, challenges arise from its nascent nature. The most prominent risks include smart contract vulnerabilities, liquidation risks, and composability risks. Interoperability of different DeFi protocols might lead to a domino effect if one protocol fails. Furthermore, the high volatility and steep learning curve of using DeFi protocols can potentially lead to significant financial losses.

In contrast, CeFi, though appearing more secure, also comes with risks, albeit more traditional, like credit risk, regulatory risk, and operational risk (cyber threats and other security issues). Your assets are held in trust by a centralized authority susceptible to internal fraud, hacking, and regulatory issues. This form of custodianship requires a great deal of trust from the user as opposed to the self-custody model in DeFi.
But as more people embrace blockchain technology, DeFi has the potential to deliver a truly global, open, and transparent financial system.

Solving global challenges with a DeFi and TradFi synergy
Despite their differences, the fusion of DeFi and TradFi could offer significant benefits to address global financial challenges. Bridging the gap between these two systems could enable accessibility, affordability, and speed in financial transactions globally. In essence, we could see a fusion of the best of both systems, fostering a global financial ecosystem that is inclusive, equitable, and resilient.
DeFi and TradFi can work together to tackle global financial hurdles. DeFi’s global accessibility and democratized decision-making meet TradFi’s regulated environment and reliability, promising a financial ecosystem that is inclusive, globally accessible, transparent yet secure, and efficient.

Financial inclusion is a key area. Billions of people worldwide lack access to basic financial services. Here, DeFi could play a huge role in providing universal access to financial services, thus bridging the financial divide. However, DeFi is alone insufficient.
TradFi, with its years of expertise in risk management, customer service, regulatory compliance, and more, can contribute significantly to this mission, thus establishing a synergy with DeFi. Transactions could be executed more seamlessly due to the blockchain, even reaching unbanked and underbanked populations, driving financial inclusion.
Furthermore, DeFi can enhance TradFi by embedding transparency, offering higher returns to stakeholders, and reducing the overall cost of operations due to its decentralized nature.
Regulatory challenges and solutions for DeFi and CeFi
Regulating DeFi and CeFi is complex due to their global reach, anonymized user base, and fast-paced technical changes. Regulations need to be precisely tailored to protect consumers and ensure market integrity, without stifling innovation. Global cooperation between regulatory authorities can help create a uniform framework that caters to these different parameters.
Operating in an avant-garde space where traditional regulatory frameworks often struggle to catch up, both DeFi and CeFi face significant challenges. DeFi, especially, with its decentralization and anonymity, presents a complex web for regulators to untangle. Emerging issues around market integrity, investor protection, and cybersecurity become increasingly critical in this new domain.
However, solutions are burgeoning. Hybrid models that combine the compelling features of DeFi with the regulatory reassurances of CeFi are increasingly common. Cross-industry collaborations can develop regulatory technology solutions, while international harmonization and cooperation among regulators globally could support the balanced growth of this field.
Rethinking crypto regulation for DeFi
The surge and evolution of cryptocurrencies and DeFi has underscored the need to rethink our approach toward regulation. Current regulatory frameworks are primarily designed for centralized systems and have trouble grappling with the decentralized nature of crypto.
Considering the unique nature of DeFi, and its potential, the need for a touch of regulation is inevitable. Rather than imposing traditional financial regulations, regulators must rethink their approach. This includes creating new models that promote transparency, security, and market integrity, while also encouraging innovation.
There has to be a shift from regulating institutions to regulating activities and behaviors. As we move towards a more decentralized financial infrastructure, regulators need to focus on decentralization’s potential risks and benefits. This includes developing mechanisms for transparency, protecting users from fraud, enforcing security measures, and ensuring tax compliance.
Striking a balance in DeFi regulation
While the regulatory challenge posed by the rise of cryptocurrencies and DeFi is considerable, it is crucial to strike a balance. On one hand, an overly lax regulatory environment can foster illicit activities and undermine global efforts to maintain financial stability. On the other hand, excessively strict regulation can stifle innovation and the potential economic benefits that these innovative technologies can deliver.
This balance can potentially be achieved by applying existing financial regulations where appropriate and developing new regulations to address the unique challenges that crypto and DeFi present. Moreover, it further underscores the need for regulatory bodies worldwide to work together in understanding and managing this rapidly developing space.
It will be a balancing act to adequately regulate without hindering the very benefits that crypto and DeFi promise, such as the democratization of finance and financial inclusion. This will require open dialogue between regulators, technologists, academics, and the industry to meet these challenges.
Bringing it all together
Through this exploration, we traced the diverse terrains of TradFi, CeFi, and DeFi, each embodying unique financial philosophies and methodologies. As we stand at the crossroads of a rapidly evolving monetary environment, we’re challenged to adapt.
We’re witnessing history in the making—a shift from familiar centralized frameworks to a world of unexplored decentralized possibilities. As these currently isolated systems blend, we anticipate a future that borrows from the tried-and-true reliability of established systems and exciting prospects of emerging technologies.
The future of finance beckons—a future that’s increasingly inclusive, transparent, and decentralized. Are we ready for the paradigm shift?
Power-boost your project on Chainstack
- Discover how you can save thousands in infra costs every month with our unbeatable pricing on the most complete Web3 development platform.
- Input your workload and see how affordable Chainstack is compared to other RPC providers.
- Connect to Ethereum, Solana, BNB Smart Chain, Polygon, Arbitrum, Base, Optimism, Avalanche, TON, Ronin, zkSync Era, Starknet, Scroll, Aptos, Fantom, Cronos, Gnosis Chain, Klaytn, Moonbeam, Celo, Aurora, Oasis Sapphire, Polygon zkEVM, Bitcoin and Harmony mainnet or testnets through an interface designed to help you get the job done.
- To learn more about Chainstack, visit our Developer Portal or join our Discord server and Telegram group.
- Are you in need of testnet tokens? Request some from our faucets. Multi-chain faucet, Sepolia faucet, Holesky faucet, BNB faucet, zkSync faucet, Scroll faucet.
Have you already explored what you can achieve with Chainstack? Get started for free today.
 Ethereum
Ethereum Solana
Solana TON
TON Base
Base BNB Smart Chain
BNB Smart Chain Sui
Sui Unichain
Unichain Aptos
Aptos TRON
TRON Ronin
Ronin zkSync Era
zkSync Era Sonic
Sonic Polygon
Polygon Gnosis Chain
Gnosis Chain Scroll
Scroll Avalanche Subnets
Avalanche Subnets Polygon CDK
Polygon CDK Starknet Appchains
Starknet Appchains zkSync Hyperchains
zkSync Hyperchains