Blockchain social media: The rise of decentralized social platforms

Social networks have served as the backbone of our digital age, catalyzing connections and communications beyond geographical limitations. However, the centralized control mechanisms of these platforms frequently compromise their virtues, leading to data breaches, privacy violations, and unwanted censorship.
To counter these insidious issues, the tech industry is increasingly turning towards blockchain technology. Thus, decentralized social networks have come into the picture.
Decentralized social networks, unlike their centralized counterparts, function on blockchain-based platforms. These cutting-edge platforms empower users by enabling them to exchange information and create and distribute content to audiences.
Operating on the blockchain, they are naturally characterized by their decentralized nature and the ensuing resistance to censorship and unwarranted control. In stark contrast to established social media services such as Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter, and Medium, these blockchain-powered networks put users first, ensuring user sovereignty and security.
Let’s explore the world of decentralized social networks and what benefits they bring.
Centralized vs decentralized social networks
Traditional social media platforms, functioning under the centralized architecture, have often faced backlashes for their opaque, autocratic decision-making, and high susceptibility to a data breach. The centralized model allows for single point-of-failure, posing significant risk.
On the other hand, decentralized social networks, built on the bedrock of blockchain technology, eliminate these risks and offer superior performance. Being part of a peer-to-peer network that spans across the globe, even if some nodes malfunction, the network remains uninterrupted.
This feature makes these systems inherently resistant to failures and outages. Leveraging blockchain technology, decentralized social networks protect user information from exploitation and unauthorized use, ensuring users won’t end up inadvertently selling their personal information to advertisers or fall prey to hackers.
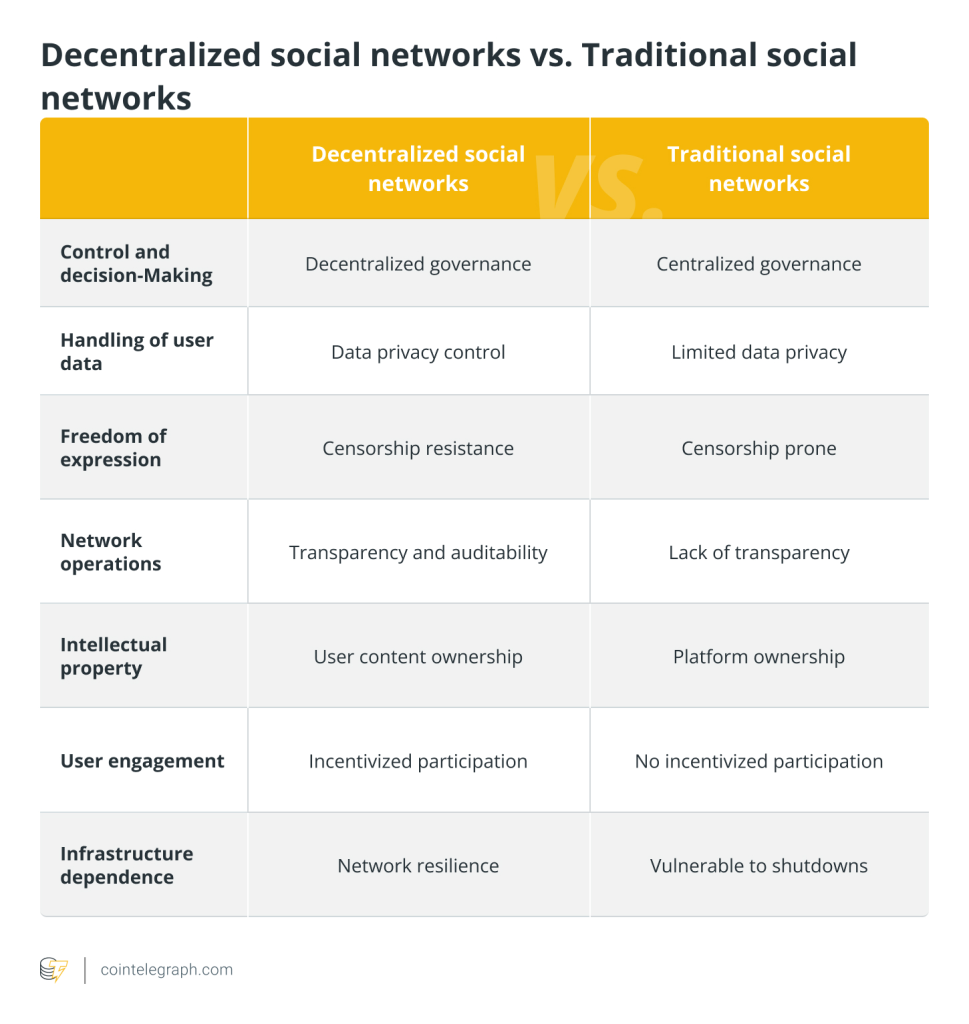
Figure 1: Decentralized social networks vs. traditional social networks; Source: CoinTelegraph
How decentralized social networks operate
Decentralized social networks represent a prime example of DApps powered by smart contracts deployed on the blockchain. The smart contract codes serve as the backbone of these platforms, outlining their logistics and business model.
Traditional social networks rely heavily on centralized databases to store user information, content, and other data forms. This mechanism creates single points-of-failure and poses significant risks. An ideal example would be the infamous outage of Facebook’s servers, resulting in users being cut off from the platform for several hours.
On the contrary, decentralized social networks are rooted in a peer-to-peer network comprising thousands of nodes worldwide. Because of this global distribution, the network operates seamlessly even if a few nodes fail, rendering it resilient to failures and outages.
Decentralized social networks utilize storage systems like the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS), offering an impregnable protection level to user data. Consequently, users can rest assured about the safety of their personal data. Many blockchain-based social platforms have also integrated native tokens into their systems to enable monetization without resorting to advertising revenues. Users can purchase these tokens to unlock certain features, complete in-app purchases, or tip their favorite content creators.
The advantages of using decentralized social networks
The advantages of decentralized social networks are multifold:
- Censorship-resistant: Decentralized social networks are open to everyone, ensuring users cannot be arbitrarily banned, deplatformed, or restricted.
- Open-source: Emboldened by open-source ideals, these networks preserve their applications’ source codes for public scrutiny. By eliminating opaque algorithms that traditional social media commonly employ, blockchain-based social networks can align users’ and platform creators’ interests more effectively.
- Direct ownership: By eliminating the middle man, decentralized social networks confer content creators with direct ownership over their content and enable them to engage directly with followers, fans, and other participants, interrupted only by a smart contract.
- Less prone to outages: As DApps running on the Ethereum network, decentralized social networks are less susceptible to server downtime and outages due to their global, peer-to-peer node network.
- Improved monetization: By integrating NFTs, in-app crypto payments, and more, decentralized social networks offer content creators an improved monetization framework.
- Enhanced privacy: Decentralized social networks afford users a high level of privacy and anonymity. For instance, an individual can sign into an Ethereum-based social network using an ENS profile or wallet—without sharing personally identifiable information (PII), such as names, email addresses, etc.
- Better safeguarding of user data: Decentralized social networks leverage decentralized storage, which is considerably better at safeguarding user data than centralized databases.
Unfortunately, as with all technologies, there are challenges and limitations to be contended with.
Challenges and limitations of decentralized social networks
As revolutionary as they may be, decentralized social networks are not without their unique set of limitations and growth complications:
- Technological understanding: Understanding and adopting blockchain technology and the concepts of DApps, cryptocurrencies, and digital wallets can be a demanding task for the average user. The complexity of blockchain concepts can act as a barrier to entry for many.
- Scalability: The scalability issue is ubiquitous across blockchain platforms, affecting Ethereum-based decentralized social networks as well. As the number of users grows, the speed of operations can be significantly reduced.
- Transaction fees: Every operation on the network, except reading data, requires token-based transaction fees (“gas” on the Ethereum network). Since these fees fluctuate based on network congestion, it could deter a good portion of prospective users.
- Public perception of cryptocurrency: Despite growing recognition, cryptocurrencies are still often associated with fraudulent activities and speculative investments, deterring some potential users.
- Regulatory approvals: With governments worldwide debating over cryptocurrency regulations, the legal standing of decentralized social networks may face future challenges.
- Digital divide: Global population segments without access to consistent internet and modern technological devices could be left at a disadvantage, potentially exacerbating the digital divide.
Despite these challenges, various innovative decentralized social networks have emerged and flourished. In the next section, let’s shine a light on some notable examples of decentralized social networks that have been successful in bringing about positive change in the world of social networking.
Notable examples of decentralized social networks
Let’s look at some decentralized social networks that are paving new paths in the realm of digital communication:
- Friend.Tech: Recently launched on Coinbase’s Base, a new layer 2 network, Friend.Tech offers a novel concept in Web3 social interaction. This platform allows users to tokenize their online personas, enabling others to buy “shares” in them. Owning shares grants access to private chats, with the share value varying based on market dynamics.
- Lens Protocol: Developed by the creators of Aave in 2022, Lens Protocol is a decentralized social graph platform enabling creators to fully own their content. It empowers users with tools to build their social media platforms using advanced Web3 technology. This innovative approach facilitates the creation of unique, user-controlled social media experiences, emphasizing content ownership and decentralization within the social media ecosystem.
- Peepeth: A microblogging platform similar to Twitter, Peepeth is built on the Ethereum blockchain and leverages IPFS for secure user data storage. Users can send “Peeps”—concise messages that once sent, are immutable, emphasizing the permanence of words. Tipping is made easy, with users able to tip their favorite content creators in Ether directly from the app.
- Pixelfield: Launched in 2018 as a decentralized alternative to Instagram, Pixelfield places a strong emphasis on user data control and privacy. The platform ensures the confidentiality of users’ images and offers an ad-free experience. Built with decentralization in mind, Pixelfield represents a shift towards more secure and user-centric photo-sharing services.
- Mirror: Mirror serves as a decentralized writing platform designed with the user-centric ethos in mind. Apart from free reading and writing by simply connecting wallets, Mirror opens up avenues for writers to mint their posts into NFTs—preserving their work indefinitely on the blockchain.
- MINDS: MINDS is one of the most prominent names in the decentralized social network sphere. Functioning similarly to Facebook, MINDS has garnered millions of users so far. The platform is underpinned by its native ERC-20 token, $MIND, which users earn by delivering popular content, enhancing the ecosystem, and referring others to the platform.
- Mastodon: As the world’s largest free, open-source, decentralized microblogging network, Mastodon presents itself as a noteworthy alternative to Twitter. It allows users to create and share brief text posts and follow others within a decentralized framework. Emphasizing its commitment to open-source development, Mastodon offers a unique social media experience that prioritizes user control and decentralization.
Integrating blockchain with traditional social media platforms
Web3 native social platforms are not the only players interested in integrating blockchain technology into their frameworks:
- Reddit: Reddit is now experimenting with Community Points—an ERC-20 token that users can earn by contributing valuable content to their community, also known as a subreddit. These tokens can be traded for special privileges and perks alongside other potential uses, thanks to its ERC-20 token nature.
- Twitter: Twitter Blue recently rolled out support for Ethereum NFTs, allowing users to display these tokens as their profile picture. The company has expressed intentions to build a decentralized version of Twitter in the future.
- Instagram: Instagram recently opened doors for Ethereum and Polygon-based NFTs. Users can directly post NFTs to Instagram by connecting their Ethereum wallet.
A common thread among all these networks is their focus on refusing centralized control, enhancing privacy, and boosting interaction. But what does the future hold for these types of social networks? Let’s explore.
The future of decentralized social networks
The entire premise of a decentralized social network is built on the belief in a more democratic and accessible internet. As we continue to grapple with issues such as privacy violations, censorship, and data monopolies, blockchain technology offers a promising solution with its inherent characteristics of decentralization and security.
Decentralized social networks can be considered an evolution in the sphere of social media as they promise to address many of the problems plaguing mainstream platforms. They prioritize user control and privacy, facilitating a sense of community that vastly transcends basic socializing and connectivity to create value.
In the future, decentralized social networks may become the new norm, ruling out the limitations of conventional platforms entirely. They may well become spaces where people will be able to freely express their ideas, own their digital assets, and earn income from their content, defining a new age of social interaction and decentralization.
Such networks are also likely to bolster the integration of newer technologies like Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) to create a more immersive user experience. Furthermore, as decentralization gains a more important place in society, a socio-economic transformation catalyzed by blockchain-based networks is very much on the horizon.
Bringing it all together
Decentralized social networks present a transformative model for social interaction, a far cry from the shortcomings of their centralized counterparts. They offer a high degree of control, privacy, and freedom, allowing for self-expression without the constraints that traditional platforms often impose.
These networks provide a fertile ground for community-driven growth, innovation, and shared economic success. Instead of entrusting control to a small group of people, decentralization seeks to distribute control among all participants, creating a social environment that prioritizes everyone’s contributions.
As we navigate the discontinuities of the digital age, decentralized social networks will only grow in importance, slowly but steadily changing the face of social media. They represent a forward-thinking approach to digital communication, taking us a step closer to a more democratic, inclusive, and user-controlled internet landscape.
The future of social networking lies in blockchain-based platforms where users aren’t sidelined but placed at the forefront of their digital experience. This vision of a more egalitarian social network isn’t far-off; it’s being built—and used—today.
Power-boost your project on Chainstack
- Discover how you can save thousands in infra costs every month with our unbeatable pricing on the most complete Web3 development platform.
- Input your workload and see how affordable Chainstack is compared to other RPC providers.
- Connect to Ethereum, Solana, BNB Smart Chain, Polygon, Arbitrum, Base, Optimism, Avalanche, TON, Ronin, zkSync Era, Starknet, Scroll, Aptos, Fantom, Cronos, Gnosis Chain, Klaytn, Moonbeam, Celo, Aurora, Oasis Sapphire, Polygon zkEVM, Bitcoin and Harmony mainnet or testnets through an interface designed to help you get the job done.
- To learn more about Chainstack, visit our Developer Portal or join our Discord server and Telegram group.
- Are you in need of testnet tokens? Request some from our faucets. Multi-chain faucet, Sepolia faucet, Holesky faucet, BNB faucet, zkSync faucet, Scroll faucet.
Have you already explored what you can achieve with Chainstack? Get started for free today.
 Ethereum
Ethereum Solana
Solana TON
TON Base
Base BNB Smart Chain
BNB Smart Chain Sui
Sui Unichain
Unichain Aptos
Aptos TRON
TRON Ronin
Ronin zkSync Era
zkSync Era Sonic
Sonic Polygon
Polygon Gnosis Chain
Gnosis Chain Scroll
Scroll Avalanche Subnets
Avalanche Subnets Polygon CDK
Polygon CDK Starknet Appchains
Starknet Appchains zkSync Hyperchains
zkSync Hyperchains