Chainstack launches support for Ethereum scaling solution Polygon

What is Polygon?
Polygon is a protocol and a framework for building and connecting Ethereum-compatible blockchain networks. Aggregating scalable solutions on Ethereum supporting a multi-chain Ethereum ecosystem, Polygon solves pain points associated with other blockchains without compromising on security, low transaction fees, and transaction speed.
In addition to technology innovation, Polygon has made building on Ethereum more accessible thanks to campaigns like the $100M #DeFiforAll fund to attract the next million DeFi participants.
Introducing Polygon support on Chainstack
We officially welcome Polygon to our platform and launch complete support for Polygon PoS mainnet and Mumbai testnet. This new offering will help developers build applications on reliable infrastructure engineered for scale in the easiest way possible on all the major public cloud providers (Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform) and geographies.
Developers will now be able to easily get access to Polygon APIs and deploy their own nodes in minutes, thereby reducing the costs associated with blockchain infrastructure and their time to market.
Having gained wide adoption within the Web3 community, the Polygon ecosystem is growing fast. Chainstack is a highly accessible and secure platform that helps businesses incorporate layer two solutions, boosting Ethereum’s transaction capacity. Polygon’s community has now a trusted ally in Chainstack to help power up experimentation, adoption, and scalability.
Eugene Aseev, Founder and CTO of Chainstack
Why Polygon on Chainstack is the right choice?
Chainstack makes running a blockchain node radically simple so that developers can focus on building their applications instead of worrying about node availability, costly maintenance, and upgrades. Chainstack as a reliable infrastructure provider is a major step forward for the Polygon ecosystem as it will allow blockchain projects to:
- Get instant access to reliable Polygon mainnet and Mumbai testnet infrastructure.
- Add advanced capabilities to any Polygon infrastructure with applications, developer tools, and services available on Chainstack Marketplace like Hardhat, The Graph, and IPFS.
- Start fast with shared Polygon nodes with multiple hosting locations, near-instant deployment, and secure HTTP and WebSocket endpoints.
- Access Polygon mainnet archive data starting at $49 per month.
- For request-intensive workload, deploy and sync dedicated Polygon nodes in minutes thanks to Chainstack-patented technology Bolt.
The rapid adoption of Polygon has resulted in the need for strong infrastructure that can support the high-throughput on-chain transactions from 300+ DApps on Polygon. We are pleased to collaborate with Chainstack to make the blockchain experience seamless for users and developers.
Sandeep Nailwal, Co-Founder and COO, Polygon
Snapshot of Polygon growing ecosystem
Having gained wide adoption within the Web3 community, the Polygon ecosystem is growing fast. Learn about the 300+ projects now on Polygon divided into a broad range of categories, with the help of these maps.
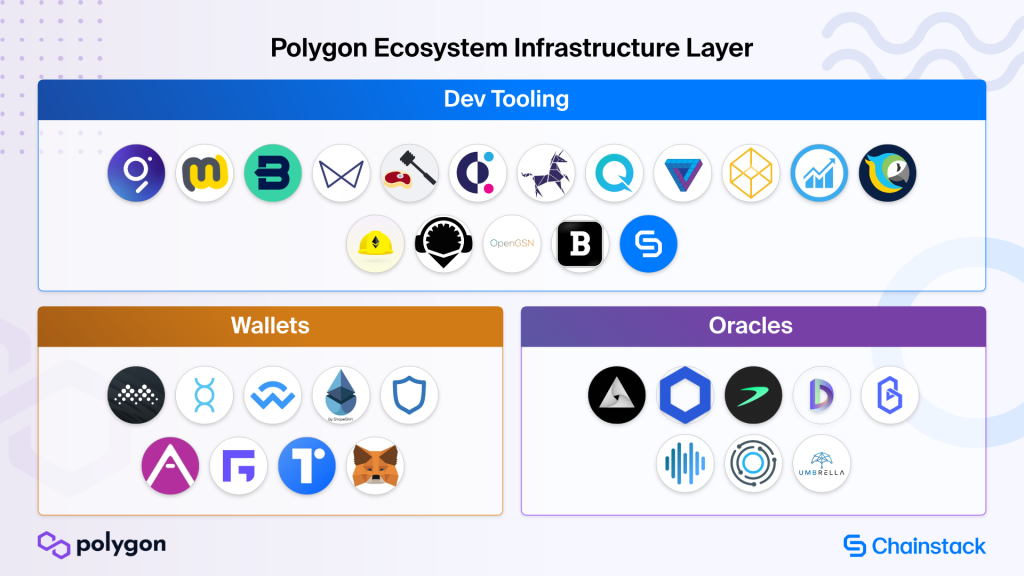
Power boosting Polygon builders
The addition of Polygon protocol in our ecosystem will mark a new frontier in Web3 deployment, offering enterprise-grade infrastructure support and flexible hosting options to one of the fastest Ethereum scaling solutions in the industry. To access a time-limited promotion and learn more about Polygon on Chainstack click here.
Connect with the community
- Explore more about using Polygon on Chainstack here.
- To start building on Polygon, follow our ERC-20 bridging tutorial.
- Sign up for a free Developer account, or explore the options offered by Growth or Business plans here.
- Take a look at our pricing tiers using a handy calculator to estimate usage and number of nodes.
- To learn more about Chainstack, visit our Knowledge Center or join our Discord server and Telegram group.
Have you already explored what you can achieve with Chainstack? Get started for free today.
 Ethereum
Ethereum Solana
Solana TON
TON Base
Base BNB Smart Chain
BNB Smart Chain Sui
Sui Unichain
Unichain Aptos
Aptos TRON
TRON Ronin
Ronin zkSync Era
zkSync Era Sonic
Sonic Polygon
Polygon Gnosis Chain
Gnosis Chain Scroll
Scroll Avalanche Subnets
Avalanche Subnets Polygon CDK
Polygon CDK Starknet Appchains
Starknet Appchains zkSync Hyperchains
zkSync Hyperchains